[▲ Imagination depicting the new spacecraft "Orion" that re -entered the atmosphere (Credit: NASA)
This is an imagination depicting a new manned spacecraft "Orion" of the American Aeronautics and Space Bureau (NASA) re -entering the atmosphere of the earth.
Currently, NASA is preparing for the manned moon exploration plan "Artemis".NASA has also been developing, as astronauts, SLS (Space Lawn System), which is used for launching Orion spaceships, which are used to launch the Earth and the moon around the moon, and the launch of Orion spaceships, etc.In the latter half of this year, we are aiming to implement the Orion spacecraft and SLS unmanned test flight "Artemis 1" mission.
Related: Successful NASA rocket "SLS" engine combustion test, one step forward for the first flight
In Artemis 1, an unmanned Orion spacecraft launched using SLS flies to the moon and returns to the earth.This mission, which is scheduled for 26-42 days, is a comprehensive test for Orion spacecraft, but according to NASA, when re -rushing into the last stage of the earth, "skip entry" (skip entry, skipping.A maneuvering method called re -entry will be tested.A skip entry is a re -entry method in which Orion spacecraft increases once on the way, like a pebble of draining play.
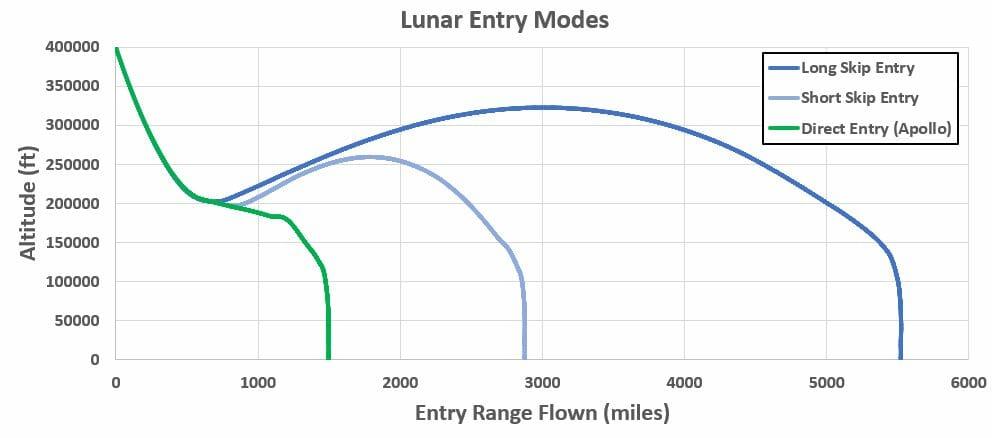
The command ship, which returned in the Apollo plan half a century ago, flew up to about 2800 km (1500 nautical areas) after re -entering and landed.On the other hand, the Artemis Plan is planned to reduce the force from the atmosphere by using the lift to reduce the ability to reduce from the atmosphere, and to fly up to 8900 km (4800 nauticals).If you control the altitude after the rise, you can adjust the flight distance, so it is said that the Orion spacecraft can accurately land in the prescribed waters no matter when you return from the month and enter the atmosphere.
When returning from the International Space Station (ISS) that goes around the earth, it is relatively easy to collect astronauts because you can select an area where you land and land at the right time to re -enter at the right time.On the other hand, in the case of an Apollo plan, which re -entered the atmosphere without going around the earth after leaving the moon, the landing area is dispersed from the North Pacific to the South Pacific, and the US Navy is an astronaut.Multiple ships had to be placed widely to recover.
The Altemis plan, like the Apollo plan, the Orion spacecraft that returned from the moon will directly enter the atmosphere, but the water area is offshore in San Diego, California, to achieve prompt recovery on a small ship.It is set to 80km sea area.Adjusting the flight distance by skip entry is the maneuvering method required to get to this sea area.In addition, in skip entry, re -entry is divided into two stages, which also has the effect of reducing the burden of acceleration on astronaut's body and heating spaceship.
According to NASA, the idea of skip entry itself was since the time of the Apollo plan, but it was not realized at the time due to technical restrictions.Altemis 1, which is scheduled for a few months, is likely to be a mission to keep an eye on from launch to landing.
[▲ A graph showing the altitude (vertical axis, feet) and flight distance (horizontal axis, miles) of the spaceship returned from the moon.The flight distance of the Orion spacecraft (light blue and blue), which is planned compared to the flight distance of Apollo spacecraft (green), is long and can be adjusted (Credit: NASA).
Related: Reuse "Atlantis" engines in the first manned flight of the new spaceship "Orion"
Image Credit: Nasasource: NASA sentence / Takehiro Matsumura
